
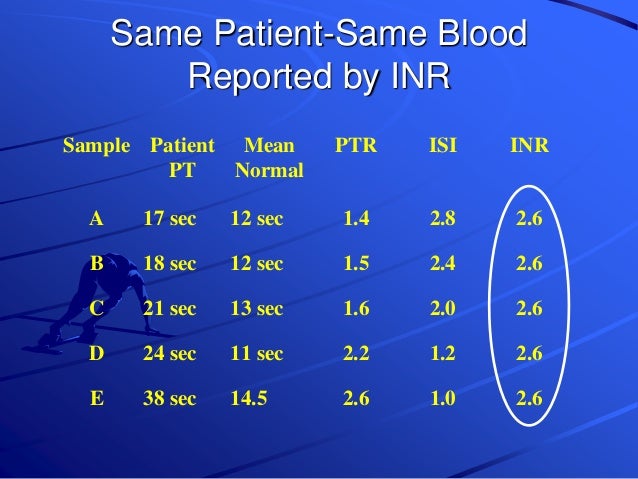
In this way, results from different laboratories and countries can be compared more readily. It takes into account the variability in results obtained using different commercial systems in calculating the result. The ISI is a numerical value representing the responsiveness of any given commercial system relative to the international standard. INR = (prothrombin test / prothrombin control) ISI So in 1983, the international sensitivity index (ISI), was applied to this ratio to derive the INR: While expressing prothrombin times compared to a control value was seen as an improvement, it was still insufficient. The control value was the average of prothrombin times from 20 or more healthy subjects. In an attempt to overcome the variability between laboratories, prothrombin times were initially expressed as a ratio of the prothrombin time of a control value. Therefore it is impossible to compare results that come from different laboratories. However, the disadvantage of this measure is that there can be large differences in the values obtained, depending on which laboratory the value was obtained from – different commercial measuring systems can produce different results. Measurement of prothrombin time has its advantages, including that it is cheap and simple to perform. Prior to this, the effects of warfarin on blood clotting were determined by a laboratory measure known as prothrombin time. It is used to determine the effects of oral anticoagulants on the clotting system.ĭevised in 1983, the INR provides a standardised method of reporting the effects of an oral anticoagulant such as warfarin on blood clotting. The international normalised ratio ( INR) is a laboratory measurement of how long it takes blood to form a clot. This is often referred to as oral anti-coagulant therapy.įor more information, see Anticoagulants. People who require long-term anticoagulant therapy are usually given warfarin, an anticoagulant that can be taken in the form of a tablet instead of injection. because they have had a stroke or heart attack previously), anticoagulants (medicines which thin the blood and reduce the formation of clots), are used to minimise the risk of blood clots forming. Therefore, when a person is at high risk of one of the above conditions (e.g. These conditions are all potentially fatal. In thromboembolic disease, fragments of blood clots dislodge and circulate in the blood, potentially obstructing blood vessels in the lungs and causing pulmonary embolism, or vessels in the heart and causing heart attack, or in the brain and causing stroke.
When this occurs, a person may be at an increased risk of thromboembolic disease. However, there are several conditions that can cause blood clots to form in the absence of active bleeding. Normally, clotting only occurs when there is blood loss from a damaged blood vessel. They are called this because they contribute to the formation of a blood clot.įor more information, see Blood Function and Composition.

Inr normal range for surgery series#
When damage occurs to a blood vessel, a series of reactions take place involving substances found in the blood known as clotting factors.
Inr normal range for surgery portable#
Health facility monitoring with a portable deviceĬoagulation or blood clotting is a protective mechanism of the body against bleeding.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
